
Global Support for Professionals
Your selection of lighting equipment will be based on such considerations as the type of results you want to achieve, the location, the weather, and the time of day.
Flash units are recommended for effective lighting. For wireless flash control involving multiple flash units, choose the SB-5000. More information is available in the Technical Guide for Radio-Controlled Advanced Wireless Lighting, available from the Nikon Download Center SB-5000 product page (https://downloadcenter.nikonimglib.com/en/products/322/SB-5000.html).
Nikon has confirmed that features such as auto white balance can produce the desired results with Nissin products and the following Profoto accessories: Profoto A1, Profoto A1X, Profoto A10, Connect, and Air Remote TTL.
Reflector panels help illuminate the faces of back-lit subjects and other areas where light tends to be lacking. Reflector panels can also be used to soften complexions and facial expressions. Add a light meter to measure light levels and calculate exposure. Other choices for diffuse lighting include diffusers and softboxes. Bring what you'll need for the task at hand.
"Point" light sources are small and "area" light sources, large. Smaller sources naturally generate harder light and shadows with sharp edges. Larger light sources, on the other hand, produce softer light and shadows with blurred edges.
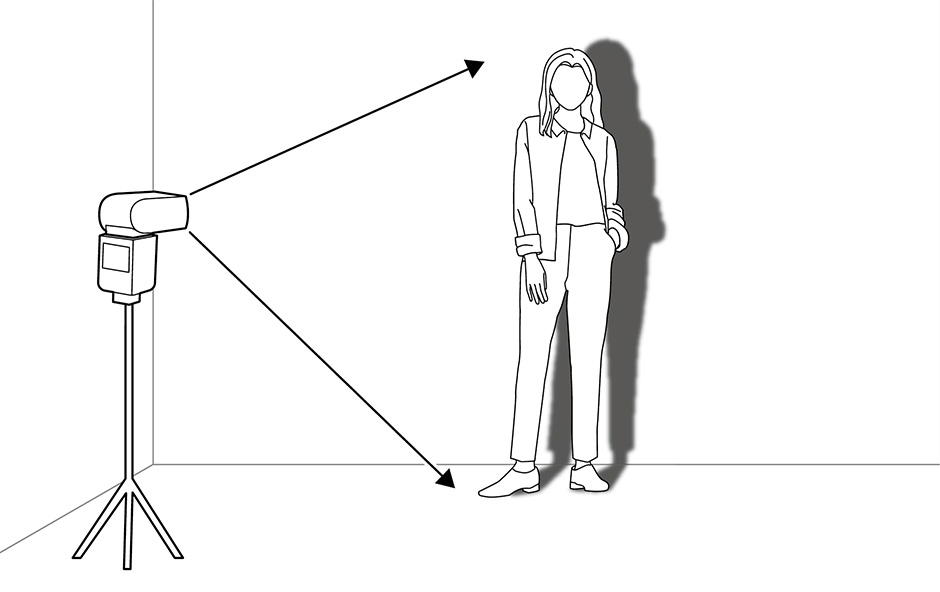
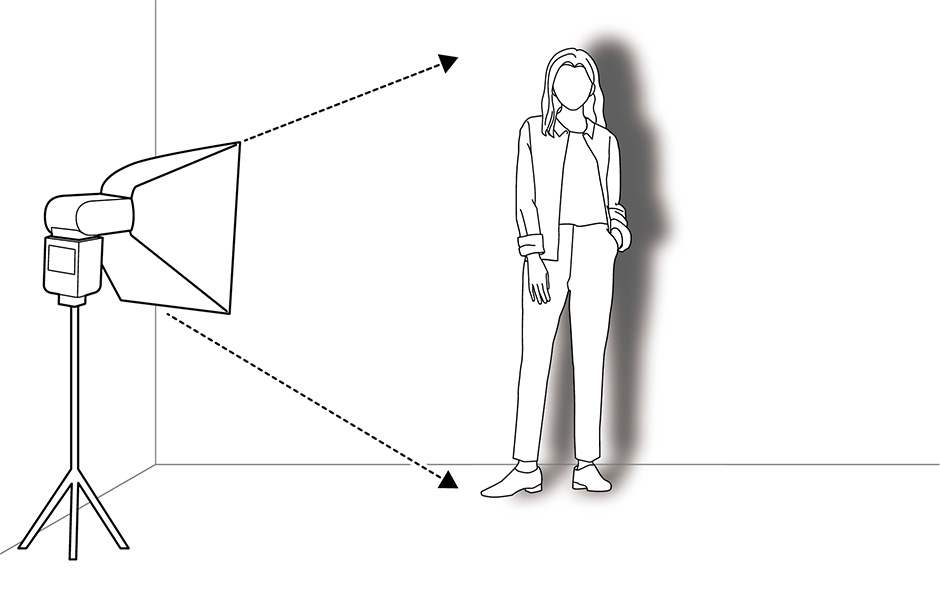
The appearance of your subject changes according to where the light is coming from.
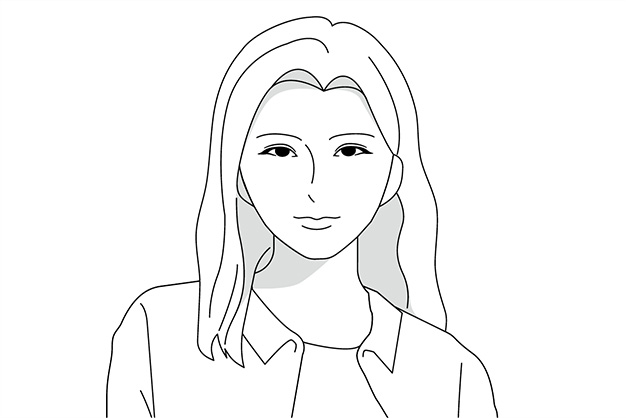
Direct lighting
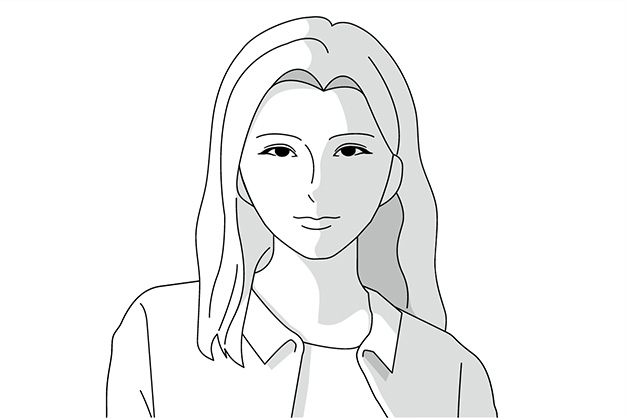

Side (oblique) lighting
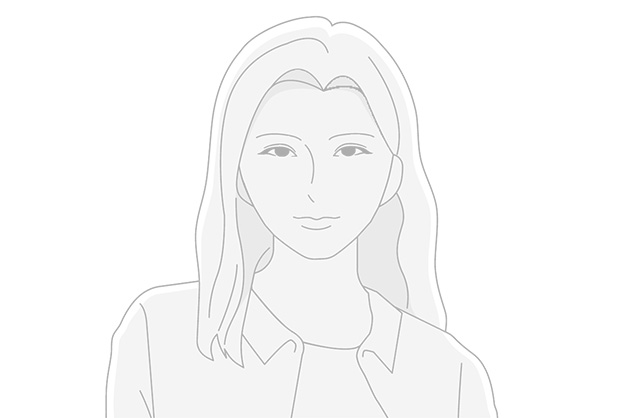
Backlighting